RMON GUI - Remote network MONitoring
Administrator handbook
|
|
RMON GUI - Remote network MONitoring
|
Table of contents |
|
Introduction to RMON - Remote Monitoring GUI
RMON stands for Remote MONitoring.
It is a standard monitoring specification that enables SNMP managers
like LoriotPro to collect network traffic statistics from RMON probes.
The LoriotPro RMON GUI program and plugin provides network administrators with comprehensive
network-fault diagnosis, traffic statistics, performance tunning.
One RMON GUI program monitors one RMON probe or one RMON capable switch. Like any other LoriotPro plugin, RMON GUI program can be started multiple times and thus can monitor multiple RMON probes or switches.
The LoriotPro RMON GUI program and plugin cannot work without RMON probe(s). The RMON probe also
called RMON agent is a dedicated device (Netscout, Sniffer distributed) including hardware or software or it
can be software embedded into a network device like a router or a switch. RMON
probe can also be software running on a standard operating system like Windows
or Linux. The application and the agent communicate across the network using
the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
The RMON specification is a set of statistics and functions define in MIB files
that can be exchanged between our LoriotPro RMON compliant manager software,
and third party RMON probes.
RMON is available in two versions, RMON1 (initially RMON) and RMON2.
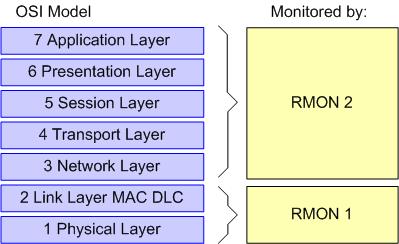
RMON1 provided traffic statistics at the MAC layer of the protocol.
LoriotPro RMON plugin supports only the Ethernet Layer. RMON1 is defined in
the RFC 1757 (Request For Comments) from the Internet Engineering
Task Force (IETF).
The RMON1 can provide statistics per Ethernet segment on : packets, and bytes received and transmitted, as well as broadcast, multicast, and error packets, source and destination address pairs and packets, bytes, and errors for each pair, top n talkers...
RMON2 extends the network traffic monitoring
to the higher protocol layers. RMON2 adds insight to those traffic statistics
by specifying the protocol and applications that compose that traffic. The traffic
knowledge is critical to deploying and troubleshooting today's client/server
environments. RMON2 extends the limited RMON1 local segment view to the global
network view.
RMON2 is defined in the RFC 2021. (RMON2 MIB)
The LoriotPro RMON plugin is RMON2 compliant and thus can show the network manager
who is talking to whom and what application(s) they are using. With this detailed
knowledge of the traffic flow in the network and how the traffic from client/server
applications is varying, the network administrator can ensure that users and
resources are located in the right network, optimize performance and discover
network usage.
 www.loriotpro.com www.loriotpro.com |
|